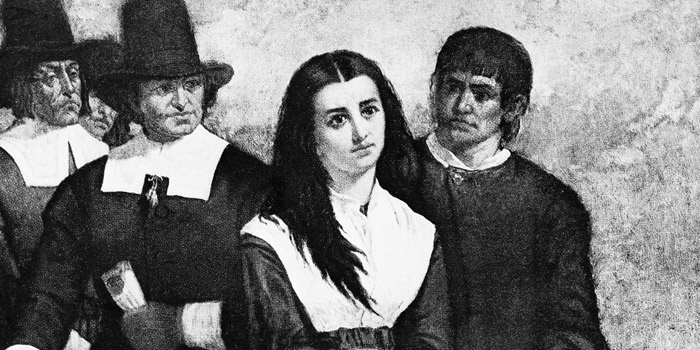
A Glimpse into a Dark Chapter of History
During the late 16th and 17th centuries, England experienced a wave of witch trials that can only be described as a frantic, often irrational, response to societal fears and personal grievances. The idea of witchcraft was deeply woven into the fabric of life, reflecting the anxieties, prejudices, and power dynamics of local communities. Women, in particular, found themselves at the heart of this hysteria, often targeted due to pre-existing village grudges, social status, or simply being different. Let’s delve into this fascinating yet tragic period of British history, exploring the cultural landscape, the key players, and the toll it took on countless lives.
Fear and Superstition: The Roots of Witch Hunts
To understand the panic surrounding witch trials, it’s essential to recognize the context of fear and superstition that permeated Britain at the time. The late 1500s were rife with social upheaval, economic instability, and a shifting political landscape. The Protestant Reformation had created fractures in society, leading to a sense of uncertainty. People needed explanations for their hardships—be it poor harvests, disease, or misfortune. Enter the witch hunts.
Witchcraft was often viewed as a direct threat to the social order. The idea that someone could be in league with the Devil and possess the power to harm innocent individuals played into the fears of the populace. Local authorities, under pressure from communities to address these fears, often found themselves grasping for scapegoats. This is where the concept of “village grudges” comes into play.
The Role of Women in Witch Trials
Women were disproportionately affected by these witch hunts. The societal norms of the time placed women in vulnerable positions, where their behavior could be scrutinized and judged harshly. Those who were widowed, poor, or otherwise socially marginalized were especially at risk. In many cases, women accused of witchcraft were simply those who didn’t conform to societal expectations.
For instance, take the case of Agnes Waterhouse, one of the first women to be tried for witchcraft in England. Accused in 1566, she was an elderly widow living alone, which made her an easy target. Her trial is a prime example of how personal grudges and societal fears culminated in tragic outcomes for women like her. Often, accusations were based on hearsay, coincidental misfortune, or longstanding feuds, with little to no evidence required for conviction.
The Mechanics of Accusation
So, how did one become an accused witch in a typical English village? The process was alarmingly simple. A person could be accused by a neighbor, often stemming from petty disputes or longstanding animosities. If misfortune struck—such as a failed crop or an illness—fingers would point in the direction of those deemed “different” or “untrustworthy.”
Once accused, the so-called witches faced harrowing trials, often characterized by a complete disregard for justice. The infamous “witch tests” included swimming a person in water; the belief was that a witch would float, as their body had been rejected by God. This absurd logic meant that many innocent women met their demise at the hands of cruel tests and public trials that prioritized spectacle over justice.
Notable Trials and Their Impact
Several trials stand out during this dark period, each a testament to the hysteria that gripped the nation. The Pendle witch trials of 1612, for example, were among the most famous in England. Twelve people from the area around Pendle Hill were accused of witchcraft, and the trials drew considerable attention, showcasing how the fear of witchcraft could spiral into community-wide panic.
Another poignant case was that of Elizabeth Sawyer, a woman accused in 1621 who was deemed a “witch” due to her elderly age and poverty. The court provided little more than hearsay as evidence, which illustrates how deeply ingrained prejudice influenced the justice system and led to the untimely deaths of many innocent women.
As these trials gained momentum, they often became spectacles that drew crowds, with the public eager to witness the alleged justice being served. The trials not only served as a means of enforcing societal norms but also as a grim reminder of the power dynamics at play in these rural communities.
The Aftermath and Societal Reflection
As the 18th century approached, the fervor surrounding witch hunts began to wane. The Enlightenment brought with it new ways of thinking, questioning superstition and advocating for reason. The excessive punishments and the irrational nature of these trials began to draw criticism from more progressive segments of society. Thinkers like John Locke emphasized reason and empirical evidence, sowing the seeds for skepticism regarding witchcraft accusations.
However, the damage had been done. The legacy of these witch hunts left a dark stain on British history, illustrating the lengths to which fear can drive individuals and communities. The women who suffered during this period were not just victims of outdated beliefs; they were often the targets of deeply personal grudges and societal pressures, reflecting the complexities of human relationships in times of crisis.
Lessons Learned: Reflections on History
Reflecting on the witch trials serves as a cautionary tale for contemporary society. Human beings have an innate tendency to seek out scapegoats during times of fear and uncertainty. This historical narrative encourages a deeper understanding of how personal bias, societal pressures, and irrational fear can lead to tragic consequences.
In a world that still grapples with issues of prejudice and scapegoating, the stories of those accused of witchcraft remind us of the importance of compassion, understanding, and due process. They beckon us to challenge the narratives spun by fear and to recognize the humanity in each individual, regardless of their differences.
Conclusion: The Need for Empathy
As we look back at Britain’s witch trial panic, we must remember the women who lost their lives to village grudges and societal fears. Their stories are not simply relics of the past; they serve as a poignant reminder of the fragility of justice and the potential for hysteria to disrupt the lives of innocent people.
By studying this dark chapter in history, we can ensure that we are vigilant against similar patterns in our own communities. Empathy and understanding are crucial in a world that continues to grapple with prejudice. Let the voices of those women echo through time, reminding us to uphold justice and humanity in the face of fear and uncertainty.
Discover more from Anglotees
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
